Search This Supplers Products:BMS Boardaluminium pcbflex PCB boardsmultilayer PCBPCB AssemblyPCB Reverse Engineering
Step into the world of printed circuit boards, let's learn more about it together!
time2021/07/07
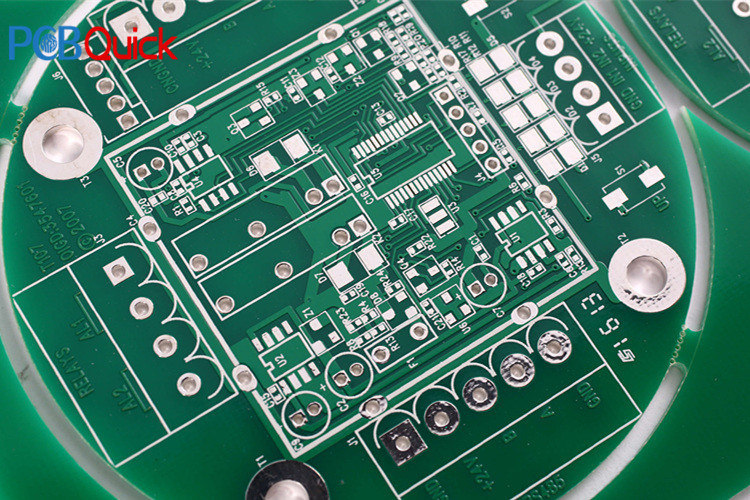
- Printed circuit boards can be divided into single-sided boards, double-sided boards, four-layer boards, six-layer boards and other multilayer circuit boards according to the number of circuit board layers. What are the differences between them?
A printed circuit board, also known as PCB circuit board, is a supplier of electrical connections for electronic components. Its development has a history of more than one hundred years; its design is based on layout design; the main advantage of using circuit boards is to greatly reduce wiring and assembly errors, and improve the level of automation and production labor.
According to the number of circuit boards, it can be divided into single-sided, double-sided, four-layer, six-layer and other multilayer circuit boards.
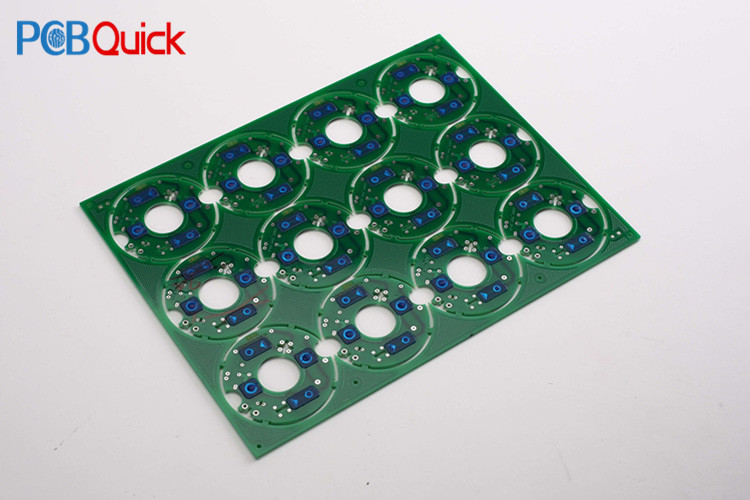
Single panel
On the most basic PCB, the parts are concentrated on one side and the wires are concentrated on the other side. Because the wires only appear on one side, this kind of PCB is called single-side. Because the single-sided board has many strict restrictions on the circuit design (because there is only one side, the wiring cannot cross, it must go around a separate path), so only early circuits use this type of board.
Double panel
This kind of circuit board has wires on both sides, but to use wires on both sides, there must be proper circuit connections on both sides. The "bridges" between such circuits are called vias. Vias are small holes filled or coated with metal on the PCB that can be connected to wires on both sides. Since the area of the double panel is twice as large as the area of the single panel, the double panel solves the difficulty of cross wiring in the single panel (via holes), and is more suitable for use in circuits that are more complex than the single panel.
Multilayer board
In order to increase the area that can be wired, single-sided or double-sided wiring boards are often used in multilayer boards. Use one double-sided as the inner layer and two single-sided as the outer layer, or two double-sided as the inner layer and two single-sided as the outer layer of the printed circuit board. The positioning system and the insulating bonding material alternate together, and the conductive pattern printed circuit boards that are interconnected according to the design requirements become four-layer and six-layer printed circuit boards, also known as multilayer printed circuit boards. The number of layers on the board does not mean that there are several independent wiring layers. In special cases, empty layers are added to control the thickness of the board. Usually, the number of layers is even, including the two outermost layers. Most motherboards are 4 to 8 layers structure, but technically speaking, almost 100 layers of PCB boards can be achieved. Most large supercomputers use fairly multi-layer motherboards, but because these types of computers can already be replaced by clusters of many ordinary computers, super multi-layer boards have gradually ceased to be used. Because the various layers in the PCB are tightly integrated, it is generally not easy to see the actual numbers, but you can still see it if you look at the motherboard carefully. Super multilayer boards have gradually ceased to be used. Because the various layers in the PCB are tightly integrated, it is generally not easy to see the actual numbers, but you can still see it if you look at the motherboard carefully. Super multilayer boards have gradually ceased to be used. Because the various layers in the PCB are tightly integrated, it is generally not easy to see the actual numbers, but you can still see it if you look at the motherboard carefully.
PCBQuick is a high-tech enterprise that exports and mass-produces printed circuit board samples. We support 24-hour online quotation and 12-hour emergency service for PCB prototypes. Specializing in the production of single-sided PCB, double-sided PCB, multilayer PCB, aluminum PCB and flexible PCB; our products are widely used in high-tech fields such as communications, computer technology, industrial control, automobiles, LED lighting, etc., and are often exported to Europe, America, Southeast Asia Well-known electronics manufacturers, Come to contact us
